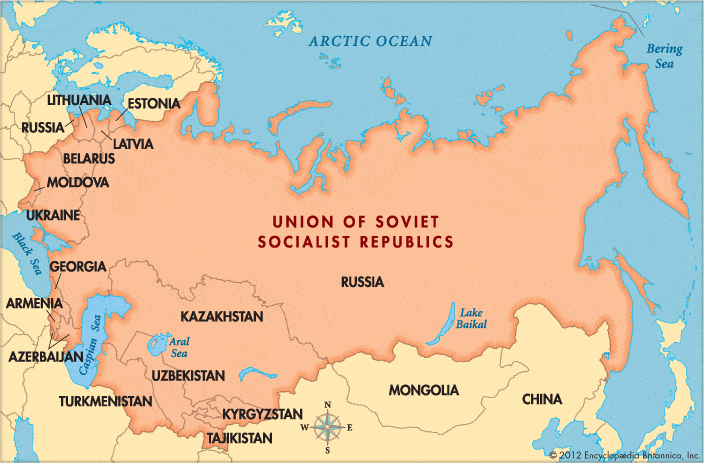
The USSR full form is the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (also known as the Soviet Union). It was formed as a northern Eurasia empire with coastlines on the Baltic and Black seas and the Arctic and Pacific oceans. It was a union of 15 Soviet social republics- Armenia, Azerbaijan, Belorussia (now Belarus), Estonia, Georgia, Kazakhstan, Kirghizia (now Kyrgyzstan), Latvia, Lithuania, Moldavia (now Moldova), Russia, Tajikistan, Turkmenistan, Ukraine, and Uzbekistan. The then capital was Moscow.
Read on to know about USSR in detail.
What Is USSR?
However, most of the population consisted of East Slavs (Russians, Ukrainians, and Belorussians), making up more than two-thirds of the total population in the late 1980s. It existed as the world’s largest country by covering an area of 22,400,000 square km, seven times the area of India and two and one-half times that of the United States. The country occupied nearly one-sixth of the Earth’s land surface in Asia.
USSR was the world’s first Marxist-Leninist state and existed between 1922 and 1991.
USSR History
Russian Revolution of 1917 resulted in the formation of the Soviet Union when the Bolsheviks led by Vladimir Lenin overthrew Russia’s Tsar Nicholas II, ending centuries of Romanov rule. A 1922 treaty between Russia, Belarus, Ukraine, and Transcaucasia (modern Georgia, Armenia, and Azerbaijan) formed the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (full form of USSR). The new Communist Party, led by Marxist revolutionary Vladimir Lenin, took control of the government.
Joseph Stalin
After the death of Lenin in1924, Georgian-born revolutionary Joseph Stalin rose to power. He ruled by terror with a series of brutal policies, which left millions of his citizens dead. Stalin transformed the Soviet Union from an agrarian society to an industrial and military superpower.
The Great Purge
Due to diminished agricultural productivity, millions died during the Great Famine of 1932-1933.
Stalin restricted all likely opposition to his leadership by terrorizing Communist Party officials and the public through his secret police.
During Stalin’s terror campaign, between 1936 and 1938, known as the Great Purge, an estimated 600,000 Soviet citizens were executed; millions were deported and imprisoned in forced labor camps known as Gulags.
The Cold War
The Soviet Union by 1948 had extended communist governments in Eastern European countries that the USSR liberated from Nazi control during World War II. A wartime alliance between the Soviet Union, the United States, and Great Britain began to creep in.
In 1949, the U.S., Canada, and its European allies formed the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), which enforced political pressure against the USSR and its allies.
Consequently, the Soviet Union in 1955 accumulated power among Eastern bloc countries under a rival alliance called the Warsaw Pact, setting off the Cold War.
Khrushchev And De-Stalinization
After Stalin died in 1953, Nikita Khrushchev rose to power during the stressed period of the Cold War. He initiated the Cuban Missile Crisis in 1962 by installing nuclear weapons just 90 miles from Florida’s coast in Cuba.
However, Khrushchev made Soviet society less repressive by initiating a series of political reforms. During the period, Khrushchev condemned Stalin for arresting and deporting opponents, took steps to raise living conditions, release many political prisoners, and loosen the Gulag labor camps, during this period known as de-Stalinization.
Sputnik
The USSR publicly launched Sputnik 1—the first-ever artificial satellite—successfully into low Earth orbit on October 4, 1957. Responding to Gagarin’s feat, U.S. President John F. Kennedy made a bold claim to put a man on the moon by the decade’s end. On July 16, 1969, astronaut Neil Armstrong became the first person to set his footsteps on the moon.
Mikhail Gorbachev
In 1985, a longtime Communist Party politician, Mikhail Gorbachev, introduced two sets of policies- Glasnost and Perestroika- to reform the political and economic systems.
The collapse of the Soviet Union
During the 1960s and 1970s, the Soviet Union’s push to industrialize at any cost resulted in frequent food and consumer goods shortages. The USSR faced attacks from foreign countries on the Soviet economy. In the 1980s, the U.S., under the leadership of Ronald Reagan, isolated the Soviet economy from the rest of the world and helped drive oil prices to their lowest levels in decades. Due to the drastic drop in the Soviet Union’s oil and gas revenue, the USSR began to lose its hold on Eastern Europe.
Consequently, on December 25, Gorbachev resigned as leader of the USSR. The Soviet Union was abolished on December 31, 1991.
By the end of the 2000 decade, some economies were five times as big as in 1991. Due to higher energy prices, major exporters like Russia, Kazakhstan, Turkmenistan, and Azerbaijan, including Moldova and Armenia, grew.
Conclusion
The USSR full form is the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (also known as the Soviet Union). It was formed as a northern Eurasia empire with coastlines on the Baltic and Black seas and the Arctic and Pacific oceans.
Here is everything you need to know about USSR in detail.
People are also Reading:

