In India, law enforcement is organized into a structured hierarchy, each rank carrying distinct responsibilities. The police force plays a pivotal role in upholding law and order in India, and its organizational structure comprises various ranks, each with distinct responsibilities.
Understanding the hierarchy of Police Ranks in India provides insights into the chain of command, illustrating the roles individuals play in maintaining the safety and security of the nation.
From the grassroots level of Constables to the leadership represented by the Director-General of Police (DGP), this exploration sheds light on the diverse roles within the Indian police system, showcasing the importance of each rank in the broader law enforcement framework.
Join us on a journey through the ranks, unraveling the intricacies of the police hierarchy and the vital contributions each position makes to the nation’s safety.
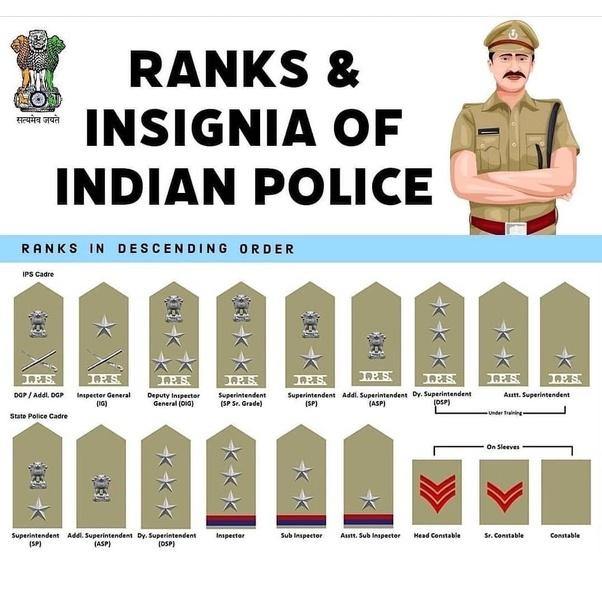 Police Ranks in India
Police Ranks in India
This article explores the various police ranks in India, shedding light on the roles and responsibilities associated with each position.
Table of Police rank
| SNo. | Police Ranks | Recruitment Method |
|---|---|---|
| 13 | Director-General of Police (DGP) | IPS through promotion |
| 12 | Additional Director General of Police | IPS through promotion |
| 11 | Inspector-General of Police (IGP) | IPS through promotion |
| 10 | Deputy Inspector General of Police | IPS through promotion |
| 9 | Senior Superintendent of Police | IPS through promotion |
| 8 | Superintendent of Police | IPS/PPS through promotion |
| 7 | Additional Superintendent of Police | IPS/PPS through promotion |
| 6 | Deputy Superintendent of Police (Dy. SP) | PPS recruited through the SPSC/IPS in the initial years |
| 5 | Inspector | Promotion |
| 4 | Sub-Inspector | Promotion |
| 3 | Assistant Sub-Inspector | Direct Recruitment through the Police Recruitment Board |
| 2 | Head Constable | Promotion |
| 1 | Constable | Direct Recruitment through the Police Recruitment Board |
1. Director-General of Police (DGP)
- The highest-ranking officer in a state or union territory.
- Responsible for overall law and order, policy implementation, and resource allocation.
The Director-General of Police (DGP) holds the highest police rank in India in the hierarchy of a state or union territory. This role is synonymous with the highest level of authority and responsibility in law enforcement.
The DGP is entrusted with the overall management of law and order, strategic policy implementation, and resource allocation within its jurisdiction.
As the head of the state police force, the DGP is pivotal in formulating and executing policies to maintain public safety and uphold the rule of law.
The Director-General of Police is responsible for overseeing the operational aspects of the police force but also for navigating complex administrative challenges. They act as a liaison between the police force and the government, providing critical insights into law enforcement needs and collaborating on initiatives to enhance public security.
The DGP’s decisions profoundly impact the functioning of the entire police apparatus, making this position instrumental in shaping the direction of law enforcement strategies and ensuring the safety and well-being of the community.
2. Additional Director General of Police (ADGP)
- Assists the DGP in managing and overseeing police operations.
- Heads specialized units or departments.
The Additional Director General of Police (ADGP) is the 2nd police rank in India in the Indian police hierarchy, serving as a key figure in the law enforcement structure. This position typically comes with a high level of responsibility, and ADGPs are often appointed to oversee specific branches, zones, or departments within a state police force.
The ADGP plays a crucial role in managing and coordinating law enforcement activities, ensuring the effective implementation of policies, and contributing to the overall strategy for maintaining public order and safety.
In addition to their operational responsibilities, ADGPs often serve as advisors to the Director General of Police (DGP). They may act as the second-in-command in the absence of the DGP. They are involved in strategic decision-making, policy formulation, and resource allocation to address law enforcement’s diverse challenges.
The role of an Additional Director General of Police requires a combination of leadership, administrative skills, and a deep understanding of law enforcement dynamics, contributing significantly to the efficient functioning of the police force and the maintenance of law and order in their designated areas of responsibility.
3. Inspector General of Police (IGP)
- In charge of various responsibilities within a zone or a big city.
- Supervises the work of Deputy Inspector Generals.
The Inspector General of Police (IGP) holds a significant and authoritative position in the law enforcement hierarchy, overseeing and managing police operations within a specific zone or department. This high-ranking officer is responsible for implementing law and order, crime prevention, and ensuring public safety in their designated jurisdiction.
The IGP collaborates with other law enforcement agencies, government officials, and community leaders to formulate and execute effective strategies for maintaining peace and security.
As a senior officer, the IGP plays a pivotal role in decision-making, policy formulation, and resource allocation within the police force. They provide leadership and guidance to subordinate officers, ensuring that the objectives of the police department align with the broader goals of the law enforcement agency. Additionally, the IGP is a crucial link between the police force and the community, fostering positive relationships and addressing public concerns.
The position demands strong leadership skills, strategic thinking, and in-depth knowledge of law enforcement practices, contributing to the effectiveness and efficiency of the police force under their command.
4. Deputy Inspector General of Police (DIG)
- Heads a range of police functions in a district or specialized division.
- Supervises Superintendent of Police.
The Deputy Inspector General of Police (DIG) holds a key leadership role in law enforcement, typically overseeing various operational functions within a specific region or specialized unit. Reporting to higher-ranking officers such as the Inspector General, the DIG is responsible for implementing and managing various aspects of policing, including crime control, investigations, and public safety.
They are vital in coordinating and supervising law enforcement activities, ensuring the department’s objectives align with broader strategic goals.
In addition to their operational responsibilities, DIGs are involved in strategic planning, policy development, and resource allocation. They work closely with other law enforcement agencies, local authorities, and community stakeholders to address issues related to law and order.
The role demands a comprehensive understanding of law enforcement practices, strong managerial skills, and the ability to make critical decisions in dynamic situations. DIGs contribute to the effectiveness of the police force by providing leadership, fostering collaboration, and ensuring the successful execution of law enforcement initiatives within their designated area of responsibility.
5. Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP) / Superintendent of Police (SP)
- In charge of district police administration.
- Manages law and order, crime prevention, and investigation.
The position of Senior Superintendent of Police (SSP) or Superintendent of Police (SP) is a crucial leadership role within the police force, responsible for overseeing law enforcement activities in a designated district or city. Serving as the top-ranking officer at the district level, the SSP/SP is tasked with maintaining law and order, preventing and investigating crimes, and ensuring community safety.
They play a pivotal role in formulating and implementing strategic initiatives to address security challenges, collaborating with local authorities, and engaging with the public to build trust and cooperation.
In addition to their operational duties, SSPs/SPs are involved in administrative tasks such as personnel management, resource allocation, and budgeting for the police department in their jurisdiction. They work closely with subordinate officers and personnel to coordinate law enforcement efforts, enforce regulations, and respond effectively to emerging situations.
The role demands strong leadership qualities, decision-making skills, and the ability to navigate complex issues to uphold public safety and the rule of law. SSPs/SPs contribute significantly to the overall effectiveness of the police force by ensuring efficient and accountable policing within their assigned geographical area.
6. Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP)
- Assists the SP in various administrative and operational duties.
- May lead police stations in smaller districts.
The Deputy Superintendent of Police (DSP) is critical in the police force, serving as a key officer responsible for managing law enforcement activities at the sub-district or subdivision level. Typically positioned as a second-in-command, the DSP supports the Superintendent of Police (SP) in maintaining law and order, preventing and investigating crimes, and ensuring public safety.
They play a vital role in the day-to-day operations of the police department, supervising subordinate officers, conducting investigations, and coordinating with other law enforcement agencies.
In addition to their operational responsibilities, DSPs are involved in administrative tasks such as managing personnel, overseeing the implementation of policies, and ensuring the efficient use of resources within their jurisdiction. They are often called upon to lead police teams during challenging situations, including crime incidents or public events requiring heightened security.
The role demands leadership skills, strategic thinking, and hands-on law enforcement experience to address the diverse challenges faced at the sub-district level effectively. DSPs contribute significantly to the overall effectiveness of law enforcement by fostering a secure environment and upholding the principles of justice and public service.
7. Inspector
- Officer in charge of a police station.
- Leads investigations and ensures law enforcement at the ground level.
The position of Inspector in the police force is a crucial and mid-level rank responsible for overseeing and executing various law enforcement duties. Inspectors are typically in charge of a police station or a specialized unit within the department, playing a pivotal role in maintaining law and order in their designated area.
They are involved in various tasks, including supervising subordinates, conducting investigations, and ensuring that all police activities align with legal and departmental regulations.
Inspectors often lead teams of officers during criminal investigations, ensuring that cases are thoroughly examined and evidence is properly collected. They also collaborate with other law enforcement agencies, handle public complaints, and participate in community policing initiatives.
Additionally, inspectors may be responsible for training and mentoring junior officers, contributing to the overall development and efficiency of the police force. The role demands leadership, analytical skills, and a deep understanding of legal procedures to effectively carry out the responsibilities associated with maintaining public safety and upholding the law.
8. Sub-Inspector (SI)
- Assists the Inspector in day-to-day operations.
- Investigate cases and maintain public order.
The Sub-Inspector (SI) is a crucial rank within the police force, holding a position that bridges the gap between lower-ranking constables and higher-ranking officers. SIs are responsible for overseeing specific units or geographical areas and play a pivotal role in law enforcement.
Their duties include investigating criminal activities, maintaining public order, and ensuring adherence to legal protocols. SIs often lead teams of constables during investigations, coordinate with other law enforcement agencies, and support higher-ranking officers in maintaining overall security.
One of the primary responsibilities of a Sub-Inspector is to conduct thorough investigations into criminal cases. They gather evidence, interview witnesses, and work closely with forensic experts to build strong cases for prosecution. SIs are also involved in routine patrolling, responding to emergencies, and handling law and order situations.
The position requires leadership, decision-making skills, and a deep understanding of criminal law. SIs serve as a critical link in the law enforcement chain, contributing significantly to the overall safety and security of the community they serve.
9. Assistant Sub-Inspector (ASI)
- Supervises the work of constables and head constables.
- Assists in investigations.
The role of the Assistant Sub-Inspector (ASI) is integral to the hierarchical structure of the police force. ASIs hold a position that combines both administrative and operational responsibilities. Reporting to higher-ranking officers, ASIs play a crucial role in the day-to-day functioning of police units.
They often supervise constables, ensure discipline within the team, and handle administrative tasks such as record-keeping and reporting.
In addition to administrative duties, ASIs are actively involved in operational tasks. They may lead small teams during investigations, conduct preliminary inquiries, and assist higher-ranking officers in maintaining law and order. ASIs act as a vital link between constables and higher-ranking officers, facilitating smooth communication and coordination within the police department.
Their versatile role demands a balance of organizational skills, leadership qualities, and a thorough understanding of law enforcement procedures. The Assistant Sub-Inspector’s position is pivotal in fostering effective police operations and upholding the principles of justice and public safety.
10. Head Constable
- The senior constable is responsible for supervising constables.
- May perform administrative duties.
The Head Constable holds a significant position within the police force, serving as a key link between higher-ranking officers and constables. A combination of administrative and operational responsibilities characterizes this role.
Head Constables supervise and guide constables, ensuring they adhere to protocols and maintain discipline. They play a crucial role in coordinating the activities of the constabulary, facilitating effective communication, and reporting to higher authorities.
In addition to their supervisory duties, Head Constables are actively involved in operational tasks. They may lead small teams during law enforcement operations, support investigations, and assist higher-ranking officers in maintaining public order. Head Constables are required to possess strong organizational and leadership skills, along with a comprehensive understanding of law enforcement procedures.
Their role is instrumental in the smooth functioning of police units, contributing to the overall effectiveness of the force in ensuring public safety and upholding the principles of justice.
11. Constable
- The entry-level position in the police force.
- Performs general policing duties.
The position of Constable is foundational within the police force, representing the frontline officers responsible for maintaining law and order. Constables are the visible presence of law enforcement in communities, patrolling designated areas, responding to emergencies, and ensuring public safety.
They play a crucial role in crime prevention, community engagement, and upholding the rule of law at the grassroots level. Constables are often the first responders to incidents, requiring them to be well-trained in handling diverse situations with a focus on public service.
Constables undergo rigorous training in various aspects of law enforcement, including criminal law, self-defense, and community relations. They are responsible for enforcing laws, conducting investigations, and assisting the public.
The role demands physical fitness, communication skills, and a commitment to upholding justice. Constables contribute significantly to building trust between the police and the community, fostering a sense of security, and ensuring that the principles of justice are upheld locally.
Conclusion
Understanding the police ranks in India provides insight into the hierarchical structure governing law enforcement. Each rank plays a crucial role in maintaining public order, preventing crime, and ensuring the safety of citizens. This article aims to demystify the organizational hierarchy of the Indian police force, highlighting the diverse responsibilities associated with each rank.
People are also reading:
