Throughout history, there have been numerous notable female mathematicians who have made important contributions to the discipline. Some of these notable figures include:
10 Famous Women Mathematicians
1. Hypatia (c. 360–415 CE)

Hypatia was a Greek mathematician, astronomer, and philosopher born in Alexandria, Egypt, circa 360 CE.
She was the daughter of Theon of Alexandria, a prominent mathematician and philosopher, who ensured she received a vital education in mathematics, astronomy, and philosophy.
Contributions to Mathematics and Astronomy
Hypatia made significant contributions to mathematics, particularly in geometry and algebra. She gained notoriety for analyzing the writings of eminent mathematicians such as Euclid and Diophantus. She also imparted knowledge in astronomy, using mathematical concepts to comprehend the motions of the stars.
2. Emmy Noether (1882–1935)

German mathematician Emmy Noether (1882–1935) contributed significantly to theoretical physics and abstract algebra. She is regarded as one of the most significant mathematicians of the 20th century, and her contributions have had a long-lasting influence on physics and mathematics.
Mathematical Contributions
Noether significantly contributed to abstract algebra, particularly in developing the theory of ideals. Her work laid the foundation for modern algebraic concepts and structures.
In physics, Noether’s fundamental theorem—now called Noether’s first theorem—connects symmetries and conservation laws. Many of the theoretical foundations of particle physics and quantum mechanics are based on this theorem. She contributed substantially to ring theory, number theory, and theoretical algebraic geometry.
3. Sophie Germain (1776–1831)

Sophie Germain was born on April 1, 1776, in Paris, France, into an upper-class family during a time when women’s formal education in mathematics was limited.
Sophie Germain (1776–1831) was a French mathematician and physicist who significantly contributed to number theory and elasticity theory.
Contributions to Number Theory
Germain is best known for her work on Fermat’s Last Theorem. She studied the theorem independently and made progress in proving specific cases, particularly when the exponent was a prime number. She corresponded with Gauss on number theory, and he highly regarded her work. However, she needed help to prove Fermat’s Last Theorem fully during her lifetime.
4. Ada Lovelace (1815–1852)

Augusta Ada King, Countess of Lovelace (1815–1852), commonly known as Ada Lovelace, was a mathematician and writer, chiefly remembered for her work on Charles Babbage’s early mechanical general-purpose computer, the Analytical Engine. Her contributions are foundational to the fields of mathematics and computer science.
Contributions to Mathematics and Computer Science:
- First Algorithm: Lovelace was the first person to program a computer when she included an algorithm for the Analytical Engine to compute Bernoulli numbers in her notes.
- Visionary Ideas: Lovelace believed that the analytical engine could be used to represent things other than numbers and manipulate symbols. This innovative concept established the foundation for the idea of a general-purpose computer.
- Poetical Science: Lovelace referred to the Analytical Engine’s capacity to produce mathematical computations, music, and art, highlighting its potential as “poetical science.”
5. Mary Cartwright (1900–1998)

Mary Cartwright (1900–1998) was a British mathematician who significantly contributed to nonlinear differential equations, non-linear oscillations, and applied mathematics. Her work established the groundwork for developments in theoretical physics and applied mathematics and significantly influenced many areas of mathematics.
Contributions to Differential Equations That Are Nonlinear:
Cartwright made important contributions to the theory of nonlinear differential equations to better understand the behavior of systems that linear equations cannot characterize.
Her work advanced our knowledge of non-linear system stability, which is important for many applications in science and engineering.
6. Julia Robinson (1919–1985)

American mathematician Julia Bowman Robinson (1919–1985) made important advances in number theory and mathematical logic. Her work on Hilbert’s tenth problem and decision problems made her most famous.
Contributions to Mathematical Logic:
- Decision Problems: Julia Robinson made important advances in studying decision problems in mathematical logic. Determining whether an algorithmic technique exists to determine whether statements made within a formal system are true or false is known as a decision problem.
- Hilbert’s Tenth Problem: Robinson’s most notable achievement was her collaboration with Martin Davis and Hilary Putnam on Hilbert’s tenth problem. This problem, posed by David Hilbert in 1900, asked for an algorithm to determine whether a given polynomial Diophantine equation (equations with integer coefficients) has integer solutions.
The trio provided a negative solution to Hilbert’s tenth problem in 1970 by demonstrating that no universal algorithm can solve all Diophantine equations.
7. Karen Uhlenbeck (1942–2019)
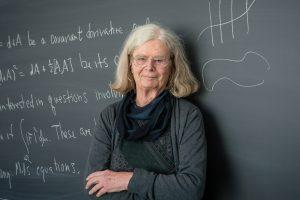
American mathematician Karen Uhlenbeck was born on August 24, 1942, and has significantly contributed to many areas of mathematics, especially partial differential equations and geometric analysis. Her work has significantly impacted the development of mathematics, and she is widely recognized for her achievements.
Contributions to Mathematics:
- Geometric Analysis: Uhlenbeck’s work has primarily studied geometric structures by applying partial differential equations and analysis tools. Her contributions to the theory of Yang-Mills connections, harmonic maps, and minimal surfaces are noteworthy.
- Yang-Mills Existence and Mass Gaps: In his research on Yang-Mills fields, which are significant in theoretical physics, Uhlenbeck worked with Jonathan Sacks. Their research on the existence of Yang-Mills equation solutions contributed to advancing theoretical physics Yang-Mills theory.
8. Sofia Kovalevskaya (1850–1891)

Sofia Kovalevskaya (1850–1891) was a Russian mathematician, the first woman to obtain a doctorate in mathematics, and a pioneer in the field. She had a difficult time going to college in the 19th century, particularly in mathematics. But Kovalevskaya was determined to get past these obstacles.
Contributions to Mathematics:
Kovalevskaya made significant contributions to the fields of analysis, partial differential equations, and mathematical physics. Her work on the rotation of rigid bodies and the dynamics of Saturn’s rings was particularly notable.
9. Ingrid Daubechies (born 1954)

Ingrid Daubechies was born in Houthalen, Belgium. She graduated from Vrije Universiteit Brussels with a Bachelor’s and Master’s degree in physics.
Belgian mathematician Ingrid Daubechies was born on August 17, 1954, and is well-known for her substantial contributions to applied mathematics, signal processing, and wavelet theory.
Contributions to Mathematics:
Daubechies has contributed to applied mathematics in addition to pure mathematics, such as creating computer graphics and image processing algorithms.
10. Maryam Mirzakhani (1977–2017)

Maryam Mirzakhani was born on May 3, 1977, in Tehran, Iran. She showed an early aptitude for mathematics and attended the International Mathematical Olympiad, winning gold medals in 1994 and 1995. Iranian mathematician Maryam Mirzakhani (1977–2017) is known for her ground-breaking work in mathematics, especially in surface geometric structure analysis.
Contributions to Mathematics:
Maryam Mirzakhani’s primary contributions were in hyperbolic geometry, Teichmüller theory, and the dynamics of geometric structures on surfaces. Her research notably impacted our knowledge of Riemann surfaces’ moduli space.
Info source all mathematicians from Wikipedia.
Conclusion
Women’s contributions to mathematics have been vital in reshaping the field, dismantling gender stereotypes, and motivating upcoming generations. Beyond their contributions to mathematics, these women have made significant contributions to the field by paving the way for greater inclusivity. Their accomplishments dispel prejudices and show that intelligence and talent are not gender-bound. The stories of these women continue to remind us that mathematics is enriched when individuals from all backgrounds and experiences contribute to its advancement.
People are also reading: