The National Testing Agency (NTA) has released the Mathematics syllabus for JEE Main 2025. This syllabus is essential for students preparing for the upcoming examination.
NTA oversees various aspects of the JEE Main examination, including releasing admit cards, result announcements, and more. Despite changes in other areas, the syllabus for Mathematics mostly remains unchanged. Familiarizing oneself with the JEE Main Maths syllabus will enable students to devise an effective study strategy for IIT JEE 2025 in an organized manner.
JEE Main Maths Syllabus 2025
| Topics | Details |
| Unit 1: Sets, Relations and Functions | Sets and their representation: Union, intersection and complement of sets and their algebraic properties; Power set; Relation, Type of relations, equivalence relations, functions; one-one, into and onto functions, the composition of functions |
| Unit 2: Complex Numbers and Quadratic Equations | Complex numbers as ordered pairs of reals, Representation of complex numbers in the form a + ib and their representation in a plane, Argand diagram, algebra of complex number, modulus and argument (or amplitude) of a complex number, square root of a complex number, triangle inequality, Quadratic equations in real and complex number system and their solutions Relations between roots and co-efficient, nature of roots, the formation of quadratic equations with given roots. |
| Unit 3: Matrices and Determinants | Matrices, algebra of matrices, type of matrices, determinants, and matrices of order two and three, properties of determinants, evaluation of determinants, area of triangles using determinants, Adjoint, and evaluation of inverse of a square matrix using determinants and elementary transformations, Test of consistency and solution of simultaneous linear equations in two or three variables using determinants and matrices |
| Unit 4: Permutation and Combination | The fundamental principle of counting, permutation as an arrangement and combination as section, Meaning of P (n,r) and C (n,r), simple applications |
| Unit 5: Binomial Theorem and its Simple Applications | Binomial theorem for a positive integral index, general term and middle term, properties of Binomial coefficients, and simple applications |
| Unit 6: Sequence and Series | Arithmetic and Geometric progressions, insertion of arithmetic, geometric means between two given numbers, Relation between A.M and G.M sum up to n terms of special series; Sn, Sn2, Sn3. Arithmetic-Geometric progression |
| Unit 7: Limit, Continuity and Differentiability | Real–valued functions, algebra of functions, polynomials, rational, trigonometric, logarithmic, and exponential functions, inverse function. Graphs of simple functions. Limits, continuity, and differentiability. Differentiation of the sum, difference, product, and quotient of two functions. Differentiation of trigonometric, inverse trigonometric, logarithmic, exponential, composite, and implicit functions; derivatives of order up to two, Rolle’s and Lagrange’s Mean value Theorems, Applications of derivatives: Rate of change of quantities, monotonic Increasing and decreasing functions, Maxima, and minima of functions of one variable, tangents and normal. |
| Unit 8: Integral Calculus | Integral as an anti-derivative, Fundamental integral involving algebraic, trigonometric, exponential, and logarithmic functions. Integrations by substitution, by parts, and by partial functions. Integration using trigonometric identities. Integral is the limit of a sum. The fundamental theorem of calculus, properties of definite integrals. Evaluation of definite integrals, determining areas of the regions bounded by simple curves in standard form. |
| Unit 9: Differential Equations | Ordinary differential equations, their order, and degree, the formation of differential equations, solution of differential equation by the method of separation of variables, solution of a homogeneous and linear differential equation |
| Unit 10: Co-ordinate Geometry | Cartesian system of rectangular coordinates in a plane, distance formula, sections formula, locus, and its equation, translation of axes, the slope of a line, parallel and perpendicular lines, intercepts of a line on the co-ordinate axis.Straight lineVarious forms of equations of a line, intersection of lines, angles between two lines, conditions for concurrence of three lines, the distance of a point form a line, equations of internal and external by sectors of angles between two lines co-ordinate of the centroid, orthocentre, and circumcentre of a triangle, equation of the family of lines passing through the point of intersection of two lines.
Circle, conic sections A standard form of equations of a circle, the general form of the equation of a circle, its radius and central, equation of a circle when the endpoints of a diameter are given, points of intersection of a line and a circle with the centre at the origin and condition for a line to be tangent to a circle, equation of the tangent, sections of conics, equations of conic sections (parabola, ellipse, and hyperbola) in standard forms, condition for Y = mx +c to be a tangent and point (s) of tangency |
| Unit 11: Three Dimensional Geometry | Coordinates of a point in space, the distance between two points, section formula, directions ratios, and direction cosines, the angle between two intersecting lines. Skew lines, the shortest distance between them, and its equation. Equations of a line and a plane in different forms, the intersection of a line and a plane, and coplanar lines. |
| Unit 12: Vector Algebra | Vectors and scalars, the addition of vectors, components of a vector in two dimensions and three-dimensional space, scalar and vector products, scalar and vector triple product. |
| Unit 13: Statistics and Probability | Measures of discretion; calculation of mean, median, mode of grouped and ungrouped data calculation of standard deviation, variance and mean deviation for grouped and ungrouped data. Probability: Probability of an event, addition and multiplication theorems of probability, Baye’s theorem, probability distribution of a random variate, Bernoulli trials, and binomial distribution. |
| Unit 14: Trigonometry | Trigonometrical identities and equations, trigonometrical functions, inverse trigonometrical functions, and their properties, heights, and distance |
JEE Mains Maths Deleted Syllabus 2025
| Topic | Details |
| Mathematical Induction | Removed from the syllabus. |
| Three Dimensional Geometry | Excluded from the updated syllabus. |
| Mathematical Reasoning | No longer part of the JEE syllabus. |
| Triangle Inequality | This topic has been dropped. |
| Square Root of a Complex Number | Excluded from the syllabus. |
| Elementary Transformations | No longer included in the syllabus. |
| Determinants | Properties of determinants are removed. |
| Binomial Coefficients | Properties are no longer part of the syllabus. |
| Special Series | Sum up to ‘n’ terms of series (Sₙ, Sₙ₂, Sₙ₃) and Arithmetico-Geometric progression are excluded. |
| Mean Value Theorems | Rolle’s and Lagrange’s Mean Value Theorems are no longer in the syllabus. |
| Integral as Limit of Sum | Excluded from the syllabus. |
| Translation of Axes | Removed from the syllabus. |
| Family of Lines | Equations for lines passing through the intersection of two lines are dropped. |
| Circle Geometry | Conditions for tangency to a circle and tangent points (y = mx + c) are removed. |
| Line and Plane Equations | Equations of a line and a plane in different forms, and intersection and coplanarity conditions are excluded. |
| Scalar and Vector Triple Product | No longer included in the syllabus. |
| Probability and Binomial Distribution | Bernoulli trials and Binomial distribution topics are removed. |
| Heights and Distances | This topic is no longer part of the syllabus. |
Best JEE Main Maths Books
| S.R | Book Name | Author | Buy Now |
| 1: | Maths for Class XI | R.D. Sharma | Click Here |
| 2: | Maths for Class XII | R.D. Sharma | Click Here |
| 3: | Algebra | Dr S K Goyal | Click Here |
| 4: | Trigonometry | S L Loney | Click Here |
| 5: | Differential Calculus | Amit M Agarwal | Click Here |
| 6: | Geometry | Arihant | Click Here |
| 7: | Trigonometry | Amit M Agarwal | Click Here |
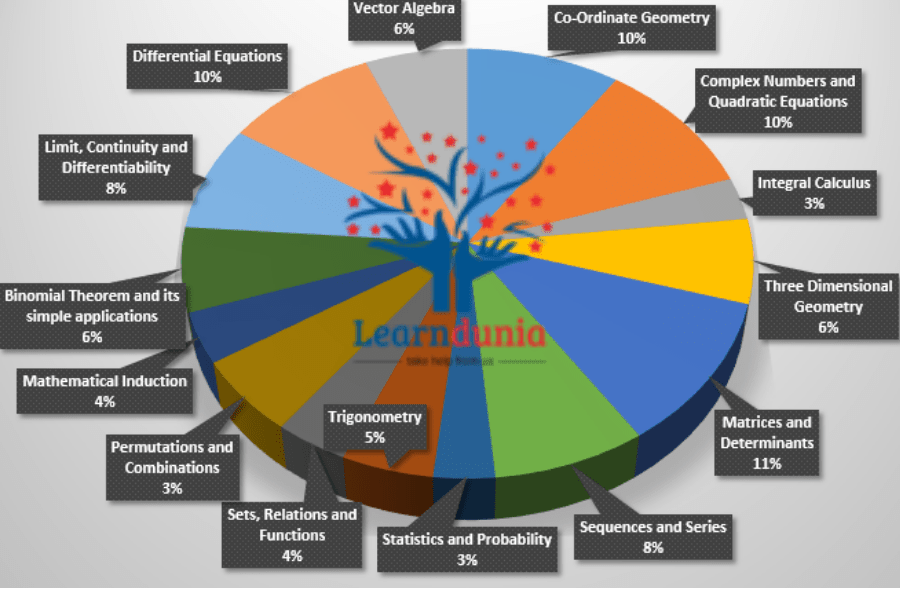
JEE Main Maths Syllabus Weightage
JEE Mathematics 2025 Preparation Tips
If you’re preparing for JEE Mains 2025, these tips can help improve your score and readiness for the actual exam:
- Understand the Syllabus: Start by familiarizing yourself with the JEE Mathematics syllabus. Create a study plan to cover the basics and practice questions. Use mock tests to simulate exam conditions and plan which questions to tackle first.
- Focus on Basics: Prepare concise revision notes with key concepts and important formulas. These are especially helpful for quick revisions before the exam.
- Practice Regularly: Scoring well in JEE Mathematics requires speed and accuracy. Regular practice will improve your efficiency and confidence.
- Time Management: Create a daily routine that includes revising important topics and solving math problems. Dedicate specific time slots to different topics to ensure balanced preparation.
- Use Good Study Material: Choose reliable resources from books or other trusted sources. Stick to the syllabus and make quick revision notes that highlight essential concepts and formulas.
- Work on Weak Areas: Identify your strengths and weaknesses. Focus on improving weaker topics while reinforcing your basics. Give extra attention to challenging areas in the syllabus.
By following these strategies, you can strengthen your preparation and perform better in the JEE Mains 2025. Click here for more tips.
Conclusion
Every year lakhs of candidates prepare for the JEE Main examination to get admission to the reputed institutions.
Mathematics is a scoring subject; students must prepare efficiently to gain good marks. Prepare effectively to escalate your final score and crack this prestigious examination.
Good luck with all your future endeavors!
People are also reading:
- Tips to Crack JEE Mains Exam
- JEE Mains Mathematics Preparation Tips
- JEE Mains Chemistry Preparation Tips
- JEE Mains Important Topics
- JEE Mains Preparation Tips
- JEE Mains Participating Institutes
- JEE Mains Cutoff for IITs
- JEE Main Practics Centers
- JEE Main Study Plan
- JEE Main Physics Preparation Tips
- Best Books for JEE Mains